Explanation of terms
Audyssey
Audyssey Dynamic EQ®
Dynamic EQ solves the problem of deteriorating sound quality as volume is decreased by taking into account human perception and room acoustics.
Audyssey Dynamic EQ® works in tandem with Audyssey MultEQ® XT to provide well-balanced sound for every listener at any volume level.
Audyssey Dynamic Surround Expansion (A-DSX)
Audyssey DSX® is a scalable system that adds new speakers to improve surround sound vividness.
Starting with a 5.1 system Audyssey DSX® first adds Wide channels for the biggest impact on envelopment. Research in human hearing has proven that information from the Wide channels is much more critical in the presentation of a realistic soundstage than the Back Surround channels found in traditional 7.1 systems.
Audyssey DSX® then creates a pair of Height channels to reproduce the next most important acoustical and perceptual cues. In addition to these new Wide and Height channels, Audyssey DSX® applies Surround Envelopment Processing to enhance the blend between the front and surround channels.
Audyssey Dynamic Volume®
Dynamic Volume solves the problem of large variations in volume level between television programs, commercials, and between the soft and loud passages of movies. Audyssey Dynamic EQ® is integrated into Dynamic Volume so that as the playback volume is adjusted automatically, the perceived bass response, tonal balance, surround impression, and dialog clarity remain the same.
Audyssey MultEQ® XT
Audyssey MultEQ® XT is a room equalization solution that calibrates any audio system so that it can achieve optimum performance for every listener in a large listening area. Based on several room measurements, MultEQ® XT calculates an equalization solution that corrects for both time and frequency response problems in the listening area and also performs a fully automated surround system setup.
Dolby
Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is a multi-channel digital signal format developed by Dolby Laboratories.
A total of 5.1-channels are played: 3 front channels (“FL”, “FR” and “C”), 2 surround channels (“SL” and “SR”) and the “LFE” channel for low frequency effects.
Because of this, there is no crosstalk between channels and a realistic sound field with a “three-dimensional” feeling (sense of distance, movement and positioning) is achieved. This delivers a thrilling surround sound experience in the home.
Dolby Digital Plus
Dolby Digital Plus is an improved Dolby Digital signal format that is compatible with up to 7.1-channels of discrete digital sound and also improves sound quality thanks to extra data bit rate performance. It is upwardly compatible with conventional Dolby Digital, so it offers greater flexibility in response to the source signal and the conditions of the playback device.
Dolby Digital EX
Dolby Digital EX is a 6.1-channel surround format from Dolby Laboratories that allows users to enjoy in their homes the “Dolby Digital Surround EX” audio format jointly developed by Dolby Laboratories and Lucasfilm.
The 6.1-channels of sound, including surround back channel, provide improved sound positioning and expansion of the surround sound field.
Dolby Pro Logic 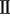
Dolby Pro Logic 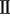 is a matrix decoding technology developed by Dolby Laboratories.
is a matrix decoding technology developed by Dolby Laboratories.
Regular music such as that on CDs is encoded into 5-channels to achieve an excellent surround effect.
The surround channel signals are converted into stereo and full band signals (with a frequency response of 20 Hz to 20 kHz or greater) to create a “three-dimensional” sound image offering a rich sense of presence for all stereo sources.
Dolby Pro Logic 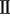 x
x
Dolby Pro Logic 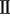 x is a further improved version of the Dolby Pro Logic
x is a further improved version of the Dolby Pro Logic  matrix decoding technology. Audio signals recorded in 2-channels are decoded to achieve a natural sound with up to 7.1-channels. There are three modes: “Music” suited for playing music, “Cinema” suited for playing movies, and “Game” which is optimized for playing games.
matrix decoding technology. Audio signals recorded in 2-channels are decoded to achieve a natural sound with up to 7.1-channels. There are three modes: “Music” suited for playing music, “Cinema” suited for playing movies, and “Game” which is optimized for playing games.
Dolby Pro Logic  z
z
Dolby Pro Logic  z introduces a new dimension to Home Entertainment through the addition of a pair of front height channels. This supports various sources such as 2-channel sources and 7.1/5.1 multi-channel sources.
z introduces a new dimension to Home Entertainment through the addition of a pair of front height channels. This supports various sources such as 2-channel sources and 7.1/5.1 multi-channel sources.
By adding height speakers to the upper left and right locations in the front of the listening environment, you can enjoy more spatial spread feel and depth feel when you play back movies/music/games.
Dolby Pro Logic  z, with front height channels is also an ideal alternative for households that cannot support the placement of back surround speakers of a typical 7.1-channel system but may have bookshelf space available to support the addition of height speakers.
z, with front height channels is also an ideal alternative for households that cannot support the placement of back surround speakers of a typical 7.1-channel system but may have bookshelf space available to support the addition of height speakers.
Dolby TrueHD
Dolby TrueHD is a high definition audio technology developed by Dolby Laboratories, using lossless coding technology to faithfully reproduce the sound of the studio master.
This format provides the facility to support up to 8 audio channels with a sampling frequency of 96 kHz/24 bit resolution and up to 6 audio channels with a sampling frequency of 192 kHz/24 bit resolution.
DTS
DTS
This is an abbreviation of Digital Theater System, which is a digital audio system developed by DTS. DTS delivers a powerful and dynamic surround sound experience, and is found in the world’s finest movie theaters and screening rooms.
DTS 96/24
DTS 96/24 is a digital audio format enabling high sound quality playback in 5.1-channels with a sampling frequency of 96 kHz and 24 bit quantization on DVD-Video.
DTS Digital Surround
DTS™ Digital Surround is the standard digital surround format of DTS, Inc., compatible with a sampling frequency of 44.1 or 48 kHz and up to 5.1-channels of digital discrete surround sound.
DTS-ES™ Discrete 6.1
DTS-ES™ Discrete 6.1 is a 6.1-channel discrete digital audio format adding a surround back (SB) channel to the DTS digital surround sound. Decoding of conventional 5.1-channel audio signals is also possible according to the decoder.
DTS-ES™ Matrix 6.1
DTS-ES™ Matrix 6.1 is a 6.1-channel audio format that inserts a surround back (SB) channel to the DTS digital surround sound through matrix encoding. Decoding of conventional 5.1-channel audio signals is also possible according to the decoder.
DTS Express
DTS Express is an audio format supporting low bit rates (max. 5.1-channels, 24 to 256 kbps).
DTS-HD
This audio technology provides higher sound quality and enhanced functionality than the conventional DTS and is adopted as an optional audio for Blu-ray Disc.
This technology supports multi-channel, high data transfer speed, high sampling frequency, and lossless audio playback. Maximum 7.1-channels are supported in Blu-ray Disc.
DTS-HD High Resolution Audio
DTS-HD High Resolution Audio is an improved version of the conventional DTS, DTS-ES and DTS 96/24 signals formats, compatible with sampling frequencies of 96 or 48 kHz and up to 7.1-channels of discrete digital sound. High data bit rate performance provides high quality sound. This format is fully compatible with conventional products, including conventional DTS digital surround 5.1-channel data.
DTS-HD Master Audio
DTS-HD Master Audio is a lossless audio format created by Digital Theater System (DTS). This format provides the facility to support up to 8 audio channels with a sampling frequency of 96 kHz/24 bit resolution and up to 6 audio channels with a sampling frequency of 192 kHz/24 bit resolution. It is fully compatible with conventional products, including conventional DTS digital surround 5.1-channel data.
DTS Neo:X
This matrix decoding technology uses the DTS Neo:X decoder to playback 2-channel source or 5.1/6.1/7.1-channel surround sources as a maximum of 9.1-channel surround sound. There are 3 modes: “Music” suited for playing music, “Cinema” suited for playing movies, and “Game” which is optimized for playing games.
Audio
ALAC (Apple Lossless Audio Codec)
This is a codec for lossless audio compression method developed by Apple Inc. This codec can be played back on iTunes, iPod or iPhone. Data compressed to approximately 60 – 70 % can be decompressed to exactly the same original data.
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC stands for Free lossless Audio Codec, and is a lossless free audio file format. Lossless means that the audio is compressed without any loss in quality.
The FLAC license is as shown below.
Copyright (C) 2000, 2001, 2002, 2003, 2004, 2005, 2006, 2007, 2008, 2009 Josh Coalson
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Neither the name of the Xiph.org Foundation nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS “AS IS” AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE FOUNDATION OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
LFE
This is an abbreviation of Low Frequency Effect, which is an output channel that emphasizes low frequency effect sound. Surround audio is intensified by outputting 20 Hz to 120 Hz deep bass to the system subwoofer(s).
MP3 (MPEG Audio Layer-3)
This is an internationally standardized audio data compression scheme, using the “MPEG-1” video compression standard. It compresses the data volume to about one eleventh its original size while maintaining sound quality equivalent to a music CD.
MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group), MPEG-2, MPEG-4
These are the names for digital compression format standards used for the encoding of video and audio. Video standards include “MPEG-1 Video”, “MPEG-2 Video”, “MPEG-4 Visual”, “MPEG-4 AVC”. Audio standards include “MPEG-1 Audio”, “MPEG-2 Audio”, “MPEG-4 AAC”.
WMA (Windows Media Audio)
This is audio compression technology developed by Microsoft Corporation.
WMA data can be encoded using Windows Media® Player.
To encode WMA files, only use applications authorized by Microsoft Corporation. If you use an unauthorized application, the file may not work properly.
Sampling frequency
Sampling involves taking a reading of a sound wave (analog signal) at regular intervals and expressing the height of the wave at each reading in digitized format (producing a digital signal).
The number of readings taken in one second is called the “sampling frequency”. The larger the value, the closer the reproduced sound is to the original.
Speaker impedance
This is an AC resistance value, indicated in Ω (Ohms).
Greater power can be obtained when this value is smaller.
Dialog normalization function
This function operates automatically during playback of Dolby Digital, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby TrueHD, DTS or DTS-HD sources.
It automatically corrects the standard signal level for individual program sources.
Dynamic range
The difference between the maximum undistorted sound level and the minimum discernible level above the noise emitted by the device.
Downmix
This function converts the number of channels of surround audio to a lower number of channels and plays back according to the system’s configuration.
Video
ISF
ISF (Imaging Science Foundation) is an organization that certifies video technicians who are then qualified to carry out calibration and adjustment to match the installation conditions. It also sets quality standards for the optimization of device video performance.
Progressive (sequential scanning)
This is a scanning system of the video signal that displays 1 frame of video as one image. Compared to the interlace system, this system provides images with less flickering and jagged edges.
Network
AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
This is a next generation standard encryption method replacing the current DES and 3DES, and because of its high security it is expected to be applied widely to wireless LANs in the future. It uses the “Rijndael” algorithm developed by two Belgian cryptographers to divide the data into blocks of fixed lengths and encrypt each block. It supports data lengths of 128, 192 and 256 bits and key lengths of 128, 192 and 256 bits as well, offering extremely high encryption security.
AirPlay
AirPlay sends (plays) contents recorded in iTunes or on an iPhone/iPod touch/iPad to a compatible device via the network.
DLNA
DLNA and DLNA CERTIFIED are trademarks and/or service marks of Digital Living Network Alliance. Some contents may not be compatible with other DLNA CERTIFIED® products.
TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol)
This is a network key used for WPA. The encryption algorithm is RC4, the same as for WEP, but the security level is increased by changing the network key used for encryption for each packet.
vTuner
This is a free online content server for Internet Radio.
For inquiries about this service, visit the vTuner site below.
vTuner website:
This product is protected by certain intellectual property rights of Nothing Else Matters Software and BridgeCo. Use or distribution of such technology outside of this product is prohibited without a license from Nothing Else Matters Software and BridgeCo or an authorized subsidiary.
WEP Key (network key)
This is key information used for encrypting data when conducting data transfer. On this unit, the same WEP key is used for data encryption and decryption, so the same WEP key must be set on both devices in order for communications to be established between them.
Wi-Fi®
Wi-Fi Certification assures tested and proven interoperability by the Wi-Fi Alliance, a group certifying interoperability among wireless LAN devices.
WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access)
This is a security standard established by the Wi-Fi Alliance. In addition to the conventional SSID (network name) and WEP key (network key), it also uses a user identification function and encrypting protocol for stronger security.
WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access 2)
This is a new version of the WPA established by the Wi-Fi Alliance, compatible with more secure AES encryption.
WPA-PSK/WPA2-PSK (Pre-shared Key)
This is a simple authentication system for mutual authentication when a preset character string matches on the wireless LAN access point and client.
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup)
This is a standard drawn up by the Wi-Fi Alliance to ease the task of setting up wireless LAN connections and configuring security. There are two methods: push-button and PIN (Personal Identification Number) code.
Network Names (SSID: Service Set Identifier)
When forming wireless LAN networks, groups are formed to prevent interference, data theft, etc. These groups are based on “SSID (network names)”. For enhanced security, a WEP key is set so that communication is unavailable unless both the “SSID” and the WEP key match. This is suitable for temporarily constructing a simplified network.
Modem
Device that connects to your broadband internet provider, and is very often supplied with the service. A type that is integrated with a router is also often available.
Media player
iTunes
iTunes is the name of the multimedia player provided by Apple Inc.
iTunes is the name of the multimedia player provided by Apple Inc. It enables management and playback of multimedia contents including music and movies. iTunes supports many main file formats including AAC, WAV, and MP3.
Windows Media Player
This is a media player distributed free of charge by Microsoft Corporation.
It can play playlists created with Ver.11 or later of Windows Media Player, as well as WMA, WAV, and other files.
Others
App Store
App Store is a site that sells application software for such devices as the iPhone or iPod Touch, and is operated by Apple Inc.
HDCP
When transmitting digital signals between devices, this copyright protection technology encrypts the signals to prevent content from being copied without authorization.
ZONE2
This unit can operate in a room other than the room where this unit is placed (MAIN ZONE) (ZONE2 playback). The room for ZONE2 playback is called ZONE2.
MAIN ZONE
The room where this unit is placed is called the MAIN ZONE.
Pairing
Pairing (registration) is an operation that is required in order to connect a Bluetooth device to this unit using Bluetooth. When paired, the devices authenticate each other and can connect without mistaken connections occurring.
When using Bluetooth connection for the first time, you need to pair this unit and the Bluetooth device to be connected.
This unit can store pairing information for a maximum of 8 devices.
Protection circuit
This is a function to prevent damage to devices within the power supply when an abnormality such as an overload, excess voltage occurs or over temperature for any reason.
If a malfunction occurs in this unit, the power indicator blinks red and the unit switches to standby mode.
